Preventing and Treating Gum Disease – What A Dentist Has To Say
One common condition we see in our patients is gum disease, which can cause severe damage to your oral health if left untreated. In this blog, I’ll discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gum disease and how to prevent it.
Causes of Gum Disease
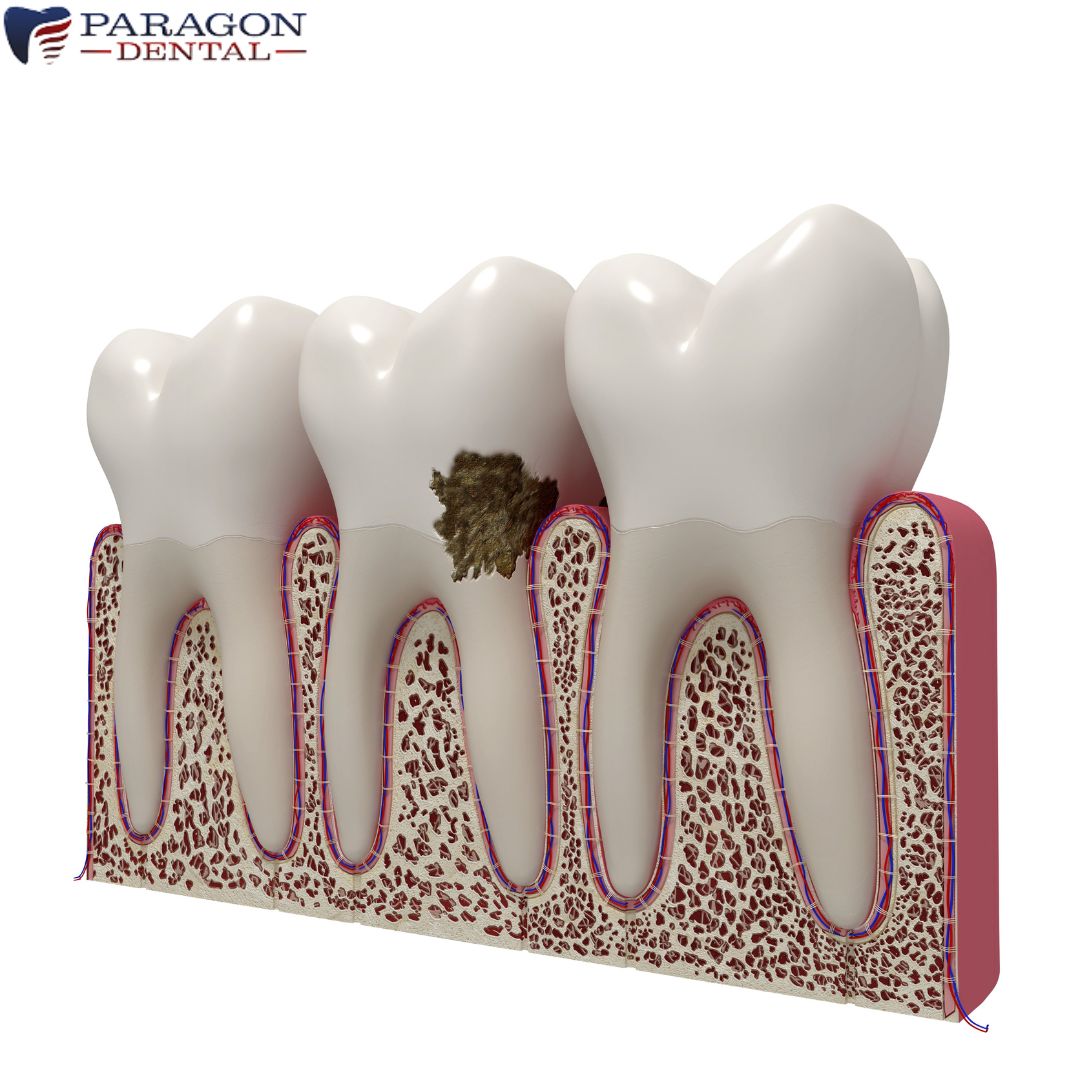
The buildup of plaque and bacteria around the teeth and gums causes gum disease. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and can harden into tartar if not removed. Tartar can cause inflammation of the gums, leading to gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Gingivitis (if left untreated) can progress to periodontitis, which can cause the loss of teeth and damage to the jawbone.
Factors that increase the risk of gum disease include poor oral hygiene, smoking, diabetes, hormonal changes in women, and genetic predisposition. It is essential to maintain good oral hygiene habits. Brushing twice daily and visiting a dentist for regular check-ups (to prevent plaque and bacteria buildup) is mandatory to avoid gum disease.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Gum disease can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums during brushing or flossing
- Receding gums or longer-appearing teeth
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Loose teeth or tooth loss
If you experience any of these symptoms, seeing a dentist for an evaluation and treatment is essential.

Treatment Options for Gum Disease
The treatment for gum disease depends on the severity of the condition. For mild cases of gum disease, treatment may involve improving oral hygiene habits, such as regular brushing and flossing and professional cleanings, to remove plaque and tartar buildup. Your dentist may also recommend antibacterial mouthwashes or gels to reduce the buildup of bacteria.
For more advanced cases of gum disease, your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing. This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line. This procedure may require multiple visits, and local anesthesia may be used to minimize discomfort.
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat gum disease. It includes procedures like gum grafts to replace damaged tissue, bone grafts to rebuild the jawbone, or flap surgery to remove tartar and bacteria from deep pockets in the gums.
Preventing Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease involves maintaining good oral hygiene and visiting the dentist regularly for cleanings and check-ups. It includes:
- brushing your teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste,
- flossing to remove plaque between teeth,
- and using mouthwash to kill bacteria that can cause gum disease.
In addition, avoid smoking, eat a balanced diet, and manage any underlying health conditions (such as diabetes) that may increase the risk of gum disease.
Conclusion
At my dental practice, we understand the importance of preventing and treating gum disease to maintain healthy teeth and gums. If you are experiencing symptoms of gum disease, don’t hesitate to schedule an appointment with us today to receive the care you need. Good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups prevent gum disease and maintain a healthy smile.

